Kanban
This gives teams more flexible Planning 1 options, faster output, clearer focus, and transparency throughout the development cycle.
> “Stop Starting! And Start Finishing!”,
The purpose of Kanban is to continually improve one’s own work process.
What is kanban?
A basic kanban board has a three-step workflow: To Do, In Progress, and Done.
Planning 1 flexibility
A kanban team is only focused on the work that’s actively in progress. Once the team completes a work item, they pluck the next work item off the top of the backlog.
The product owner is free to reprioritize work in the backlog without disrupting the team, because any changes outside the current work items don’t impact the team.
As long as the product owner keeps the most important work items on top of the backlog, the development team is assured they are delivering maximum value back to the business.
So there’s no need for the fixed-length iterations you find in scrum
How does Kanban work?
– The Concept
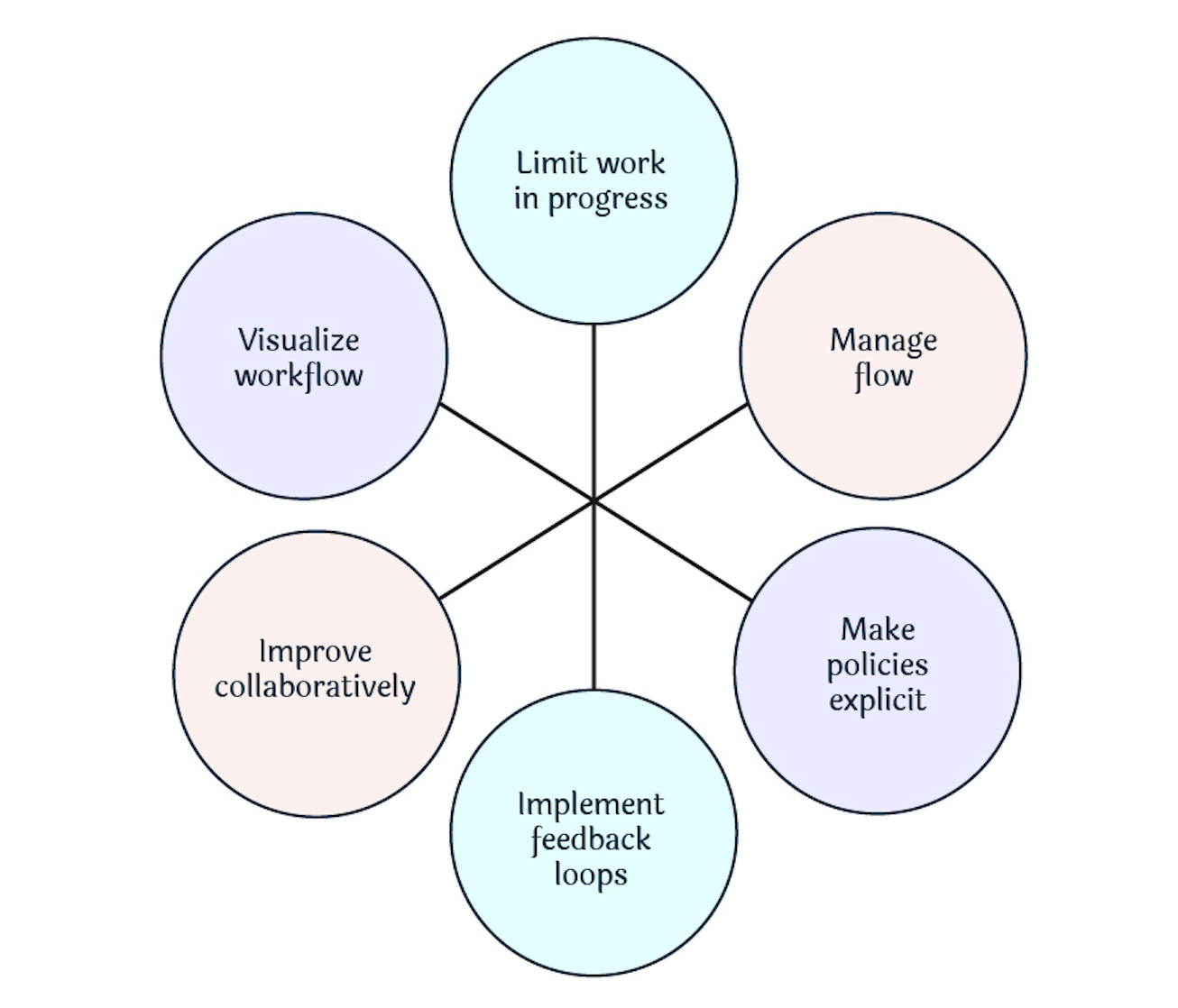
Kanban is a non-disruptive evolutionary change management system. This means that the existing process is improved in small steps.
By implementing many minor changes (rather than a large one), the risk to the overall system is reduced. The evolutionary approach of Kanban leads to low or no resistance in the team and the stakeholders involved.
The first step in the introduction of Kanban is to visualize the workflow. This is done in the form of a Kanban board consisting of a simple whiteboard and sticky notes or cards. Each card on the board represents a task.
In a classic Kanban board model, there are three columns, as shown in the picture above:
- “To Do”: This column lists the tasks that are not yet started. (aka “backlog”)
- “Doing”: Consists of the tasks that are in progress.
- “Done”: Consists of the tasks that are completed.
This simple visualization alone leads to a great deal of transparency about the distribution of the work as well as existing bottlenecks if any. Of course, Kanban boards can show elaborate workflows depending on the complexity of the workflow and the need to visualize and examine specific parts of the workflow to identify bottlenecks in order to remove them.
The concept of FLOW
At the core of Kanban is the concept of “Flow”. This means that the cards should flow through the system as evenly as possible, without long waiting times or blockages. Everything that hinders the flow should be critically examined. Kanban has different techniques, metrics and models, and if these are consistently applied, it can lead to a culture of continuous improvement (kaizen).